NASA's Solar Sail System Achieves Full Deployment in Space: The ACS3 Breakthrough
NASA's Solar Sail System Fully Deploys in Space
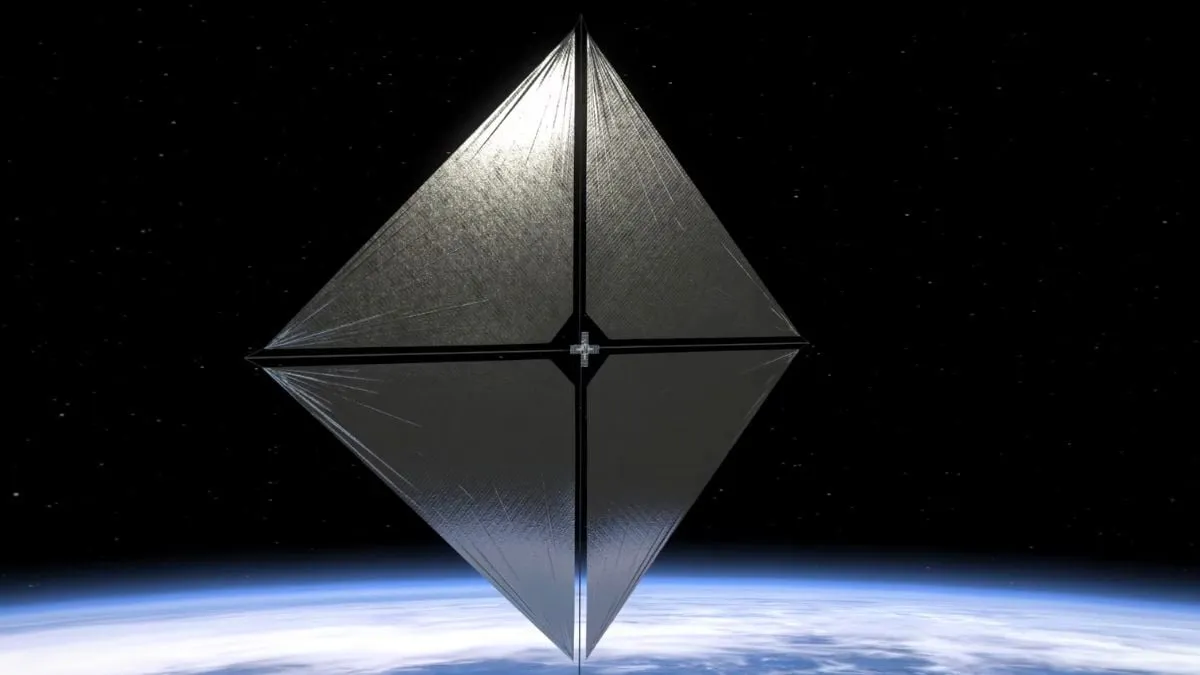
After more than four months in space, NASA's Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3) has successfully deployed its solar sail. The spacecraft, which launched aboard Rocket Lab's Electron vehicle on April 24, reached a significant milestone on August 29 at 1:33 pm EDT. The mission operators confirmed the sail's full deployment, showcasing a technology that harnesses the momentum of photons instead of conventional forces.
How the Solar Sail Works
The concept behind the solar sail is straightforward. Photons, despite having no mass, can exert pressure when they encounter an object. The ACS3's sail utilizes this photon pressure for propulsion in the depths of space. Equipped with four cameras, the spacecraft captures panoramic views of the deployed reflective sail and its composite booms, with the first high-resolution images expected by September 4.
Testing the Solar Sail in Space
The upcoming weeks are crucial for assessing the sail's capabilities, as NASA teams shift focus toward the spacecraft's maneuverability through orbital adjustments. Such maneuvers will enable the collection of valuable data, refining future solar sail designs and operations. Potential applications include early-warning satellites for space weather, reconnaissance missions targeting asteroids, and studies of the sun's polar regions.
Future Prospects for Solar Sails
Now orbiting at twice the altitude of the International Space Station (ISS), the fully deployed sail stretches out like a square nearly half the size of a tennis court, covering an area of approximately 860 square feet (80 square meters). This success is a promising leap towards utilizing solar sails for diverse space missions in the future.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.