Innovative Multi-Class Machine Learning Method Enhances Taste Sensation Prediction
Understanding Taste Perception
Taste perception is vital for guiding nutrient intake and avoiding harmful substances, relying on five basic tastes: sweet, bitter, umami, salty, and sour. This perception arises from interactions between taste receptors and chemical tastants in the mouth.
Advancements in Machine Learning
Recent developments have introduced algorithms that classify the tastes of chemical compounds based on their molecular structures. Despite progress, improvements are still needed for multi-class models to predict the full spectrum of basic tastes.
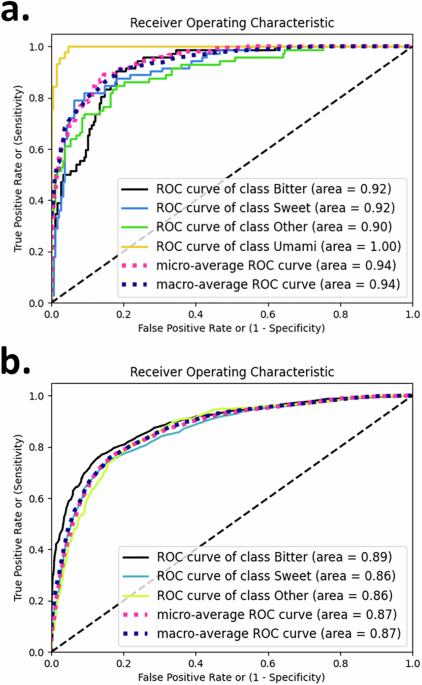
Introducing the Multi-Class Predictor
- This study presents a multi-class predictor that distinguishes between bitter, sweet, and umami tastes from other sensations.
- Such a predictor enhances the understanding of chemical attributes linked to each fundamental taste.
Future Implications
This method holds the potential to integrate with multi-sensory perception, which includes visual and olfactory sensations, for a comprehensive flavor characterization.
- Improving food design methodologies.
- Predetermining specific tastes.
- Engineering complementary diets alongside traditional treatments.
The development of this multi-class taste predictor represents a significant leap towards enhancing food design and dietary management.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.