Exploring the Role of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Alcohol Dependence and Addiction
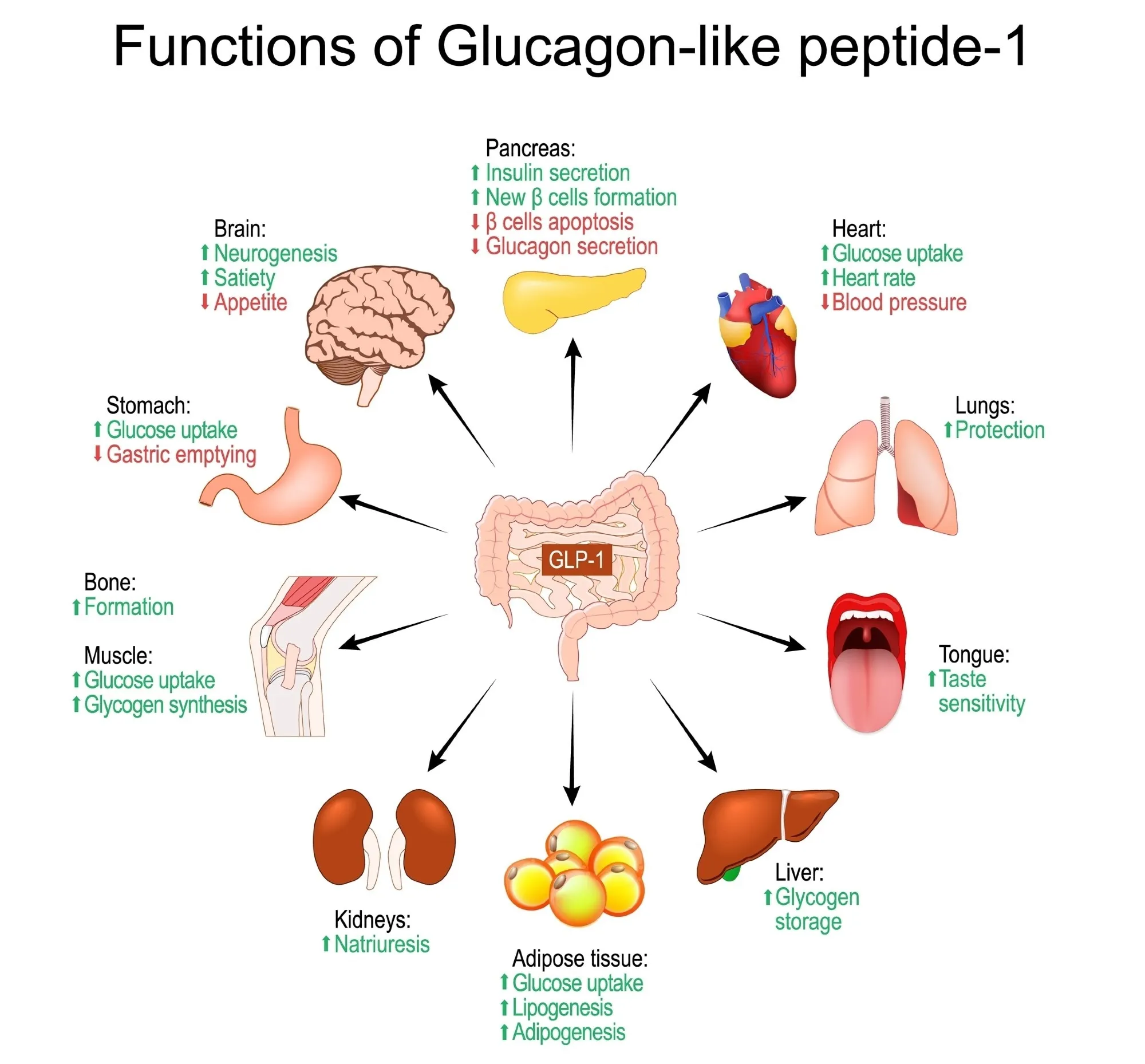
Introduction to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as a potential treatment for various substance use disorders. These medications, which mimic glucagon-like peptide-1, may significantly impact addiction treatment protocols.
Effects on Alcohol Dependence
Research indicates that GLP-1 receptor agonists could help mitigate alcohol cravings and reduce consumption, leading to improved outcomes for individuals struggling with alcohol dependence.
Link to Metabolic Health
- Glycated hemoglobin levels may also improve with treatment.
- Increased understanding of the connections between obesity and addiction is crucial.
Potential for Broader Applications
Beyond alcohol dependence, there's growing interest in the effects of GLP-1 on other addictive substances, such as nicotine. The multifaceted nature of these receptors suggests that they could play a role in managing broader substance use disorders.
Implications for Public Health
The application of these findings on public health should not be understated; targeting the brain's response to addiction could lead to more effective treatment approaches and a potential decrease in mortality linked to overdose.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.