BMC Urology: Enhanced Outcomes in Staghorn Stone Treatment with Double-J Stent and PCNL
Research Findings on PCNL and Staghorn Stones
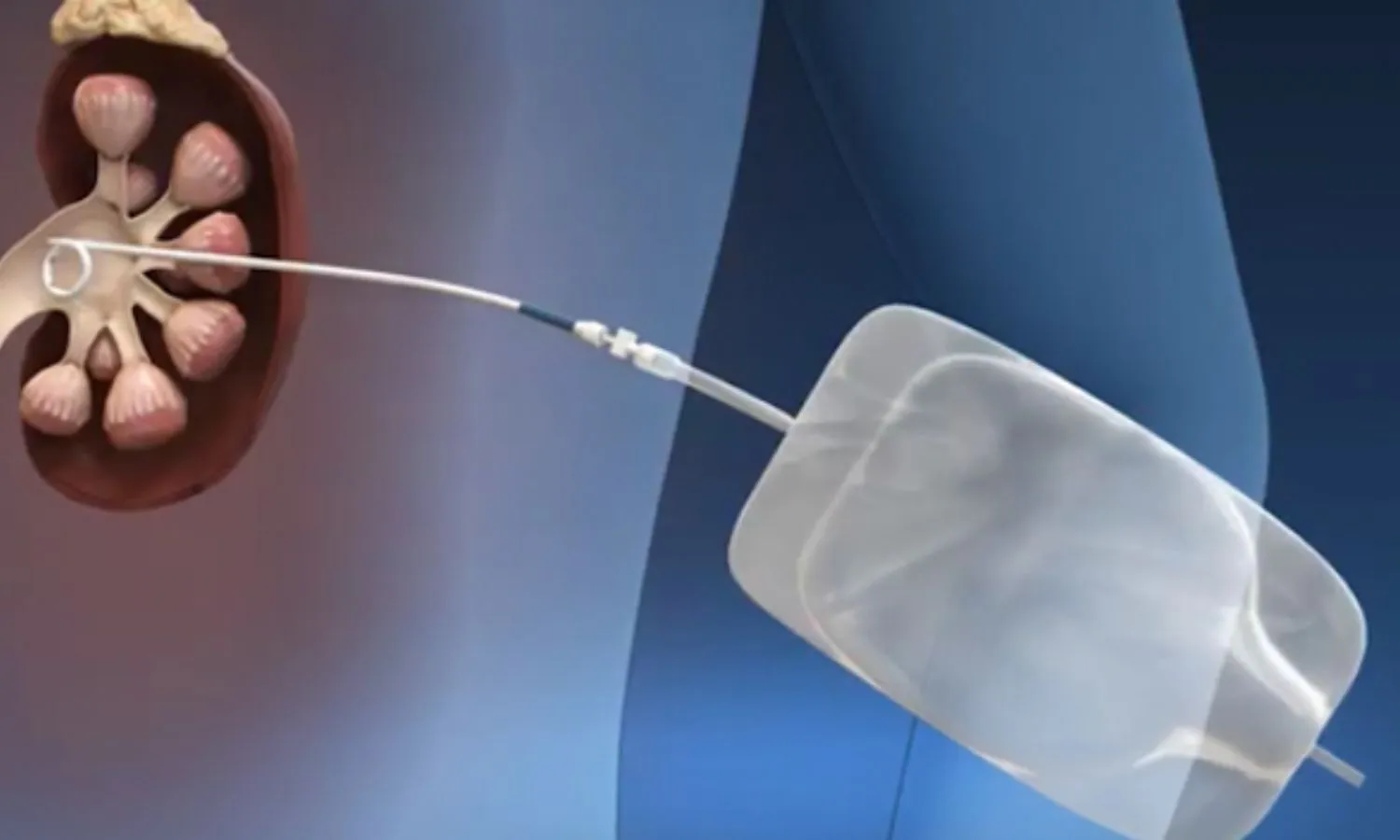
The recent study featured in BMC Urology suggests that implementing a double-J stent following the procedure of percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) offers improved results for treating staghorn stones. The authors emphasize that the omission of this stent typically delivers adequate outcomes; however, it correlates with higher residual stone rates, potentially elevating post-operative complications.
Importance of Double-J Stent in PCNL
- PCNL is a widely accepted procedure for the management of renal stones.
- Double-J stents can enhance drainage and reduce complications associated with stone residue.
- Patients with staghorn stones may benefit significantly from using ureteral catheters post-surgery.
Further research is encouraged to evaluate the long-term implications of stent use in patients undergoing PCNL.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.