Medicine Research: Understanding Brain Processes in Schizophrenia and Auditory Hallucinations
Groundbreaking Findings in Schizophrenia Research
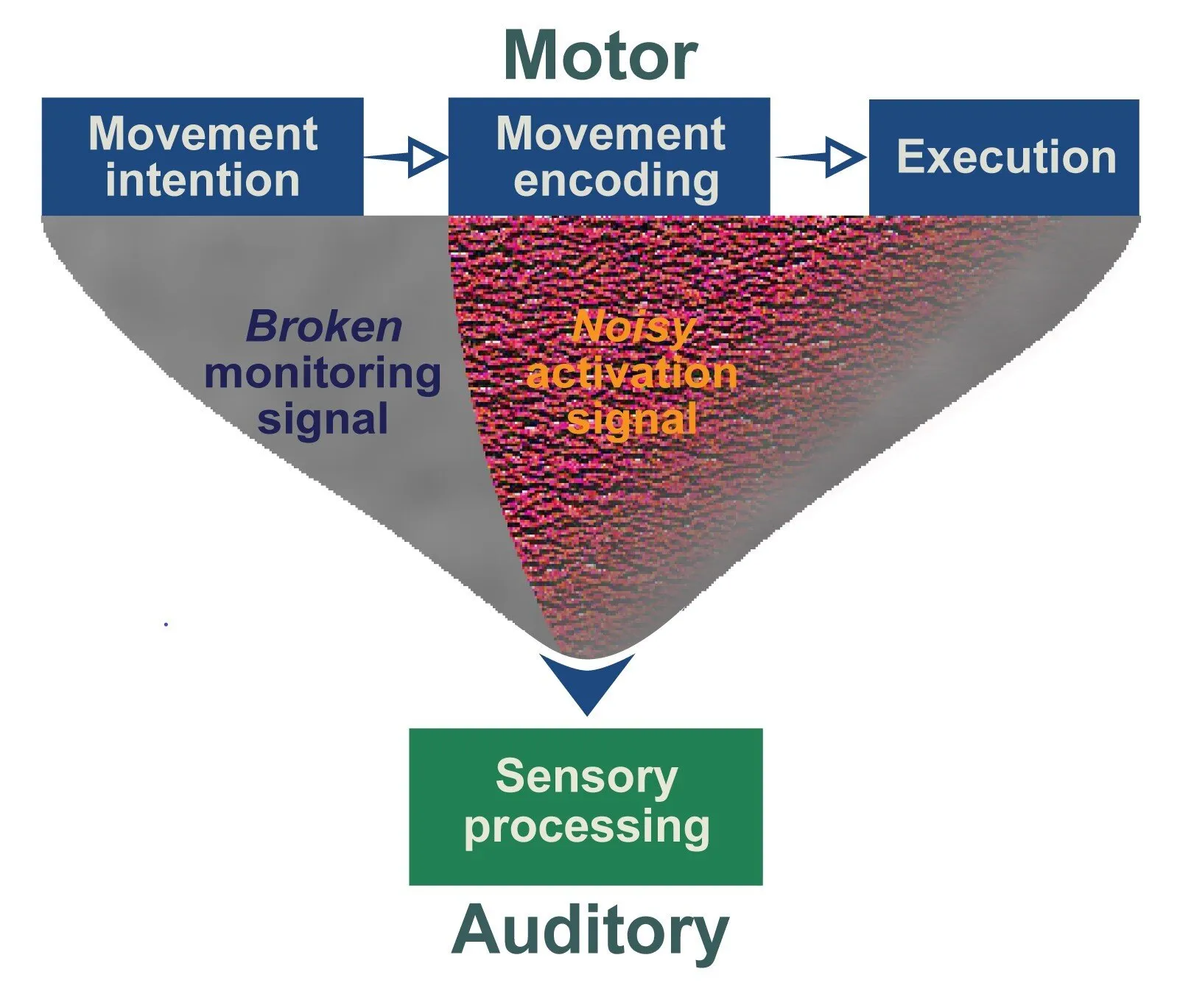
A recent study utilizing brain scans has shed light on the intricate processes occurring in the brains of individuals with schizophrenia, particularly when they experience auditory hallucinations. The research suggests that these hallucinations result from two primary abnormalities: a corollary discharge that becomes disrupted, leading to an inability to suppress self-generated sounds, and a noisy efference copy that inaccurately processes external auditory input.
Implications for Treatment and Understanding
These findings could pave the way for innovative therapeutic approaches in treating auditory hallucinations. The identification of the specific brain mechanisms involved may enhance future health research efforts and lead to advanced medical interventions.
Future Directions in Medicine Science
Continued exploration within this branch of health science could reveal more about the neurobiological underpinnings of schizophrenia and help refine health policies concerning mental health treatments.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.