Science Reveals How Low Gravity in Space Affects Heart Muscle Cells
Science News: Impact of Low Gravity on Heart Health
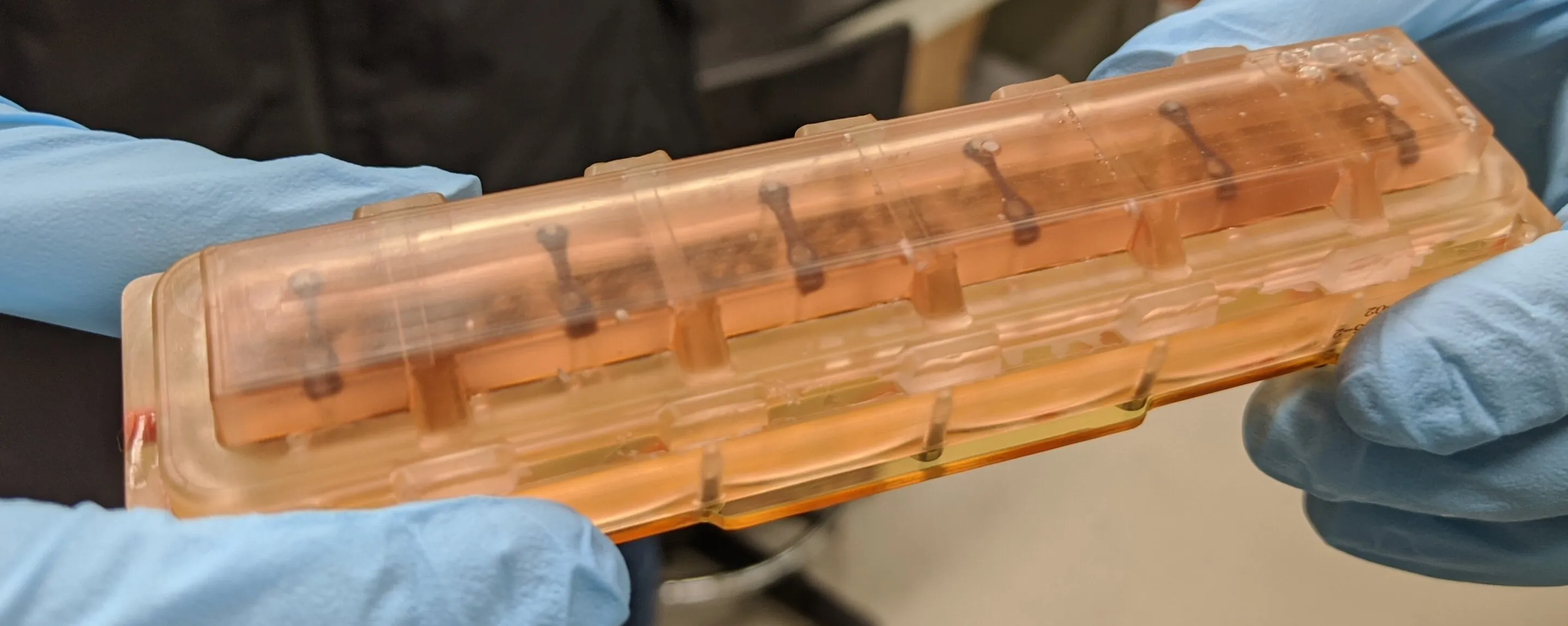
Recent research conducted by Johns Hopkins Medicine illustrates how low gravity conditions encountered during space travel can severely disrupt and weaken the normal rhythm in heart muscle cells. For 30 days, 48 human bioengineered heart tissue samples were subjected to the unique environment aboard the International Space Station.
Key Findings of the Study
- Breakthrough Evidence: Low gravity led to structural changes in heart tissues.
- Potential Risks: Astronauts may face increased cardiovascular health issues.
- Importance of Nanotech in combating these challenges.
As space travel becomes more common, addressing these cardiac concerns is crucial for ensuring astronaut health. This pioneering study opens avenues for further research on materials and technologies that can mitigate health risks in prolonged low-gravity environments.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.