Deadly Fungal Infections: Understanding the Silent Pandemic Threat
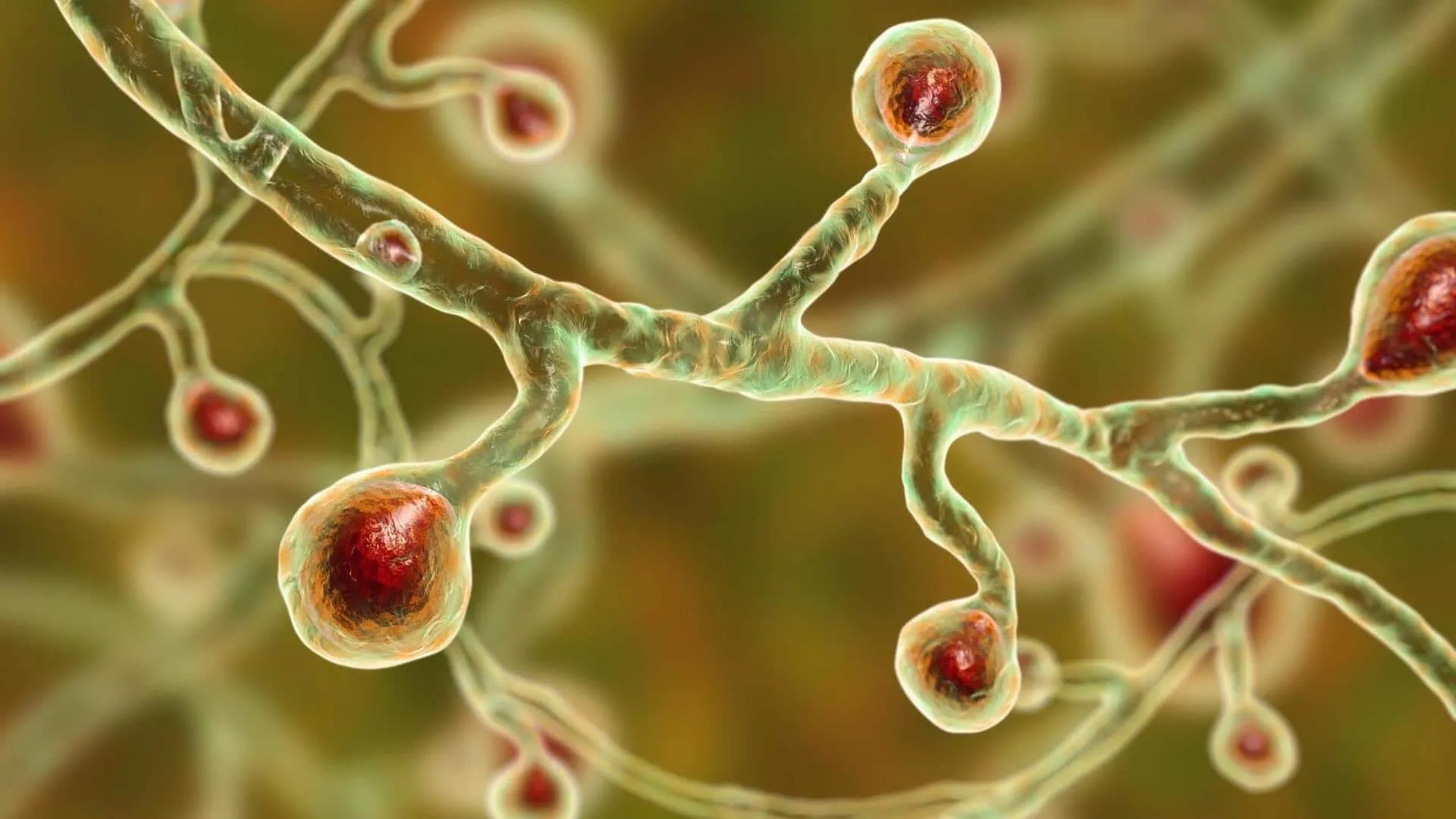
The Global Health Crisis of Fungal Infections
Deadly fungal infections are indeed becoming a serious global health crisis. According to molecular biologist Norman van Rhijn from the University of Manchester, the threat of antifungal resistance is often neglected in worldwide discussions about antimicrobial resistance. This oversight is alarming given that aggressive fungal infections currently impact 6.5 million people every year, resulting in 3.8 million deaths.
Urgent Call for Action
The team of researchers argues that the growing problem of fungal pathogens should be central to discussions on antimicrobial resistance, especially with the upcoming meeting hosted by the United Nations in New York City.
- Resistance is becoming increasingly common in existing antifungal treatments.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) released its first Fungal Priority Pathogen List in 2022, prioritizing dangerous fungal species.
- Highlighted fungi include Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida, Nakaseomyces glabratus, and Trichophyton indotineae.
The Complexity of Fungal Pathogens
Fungi are complex organisms, sharing structural similarities with animals. This complexity makes it challenging for researchers to develop effective antifungal medications that eradicate fungal cells without harming human cells.
- Only four systemic antifungal classes are currently available for treating serious fungal infections.
- There is a pressing concern that drug resistance may exacerbate before new antifungals reach the market.
Balancing Food Security and Health
As the agrochemical industry accelerates the development of new antifungals, there is a risk of cross-resistance for critical pathogens. This highlights an ongoing need for balance between food security and the treatment of resistant fungal infections.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.