HIV, TB, and Malaria: UNGA's Commitment to Sustainable Development Goals
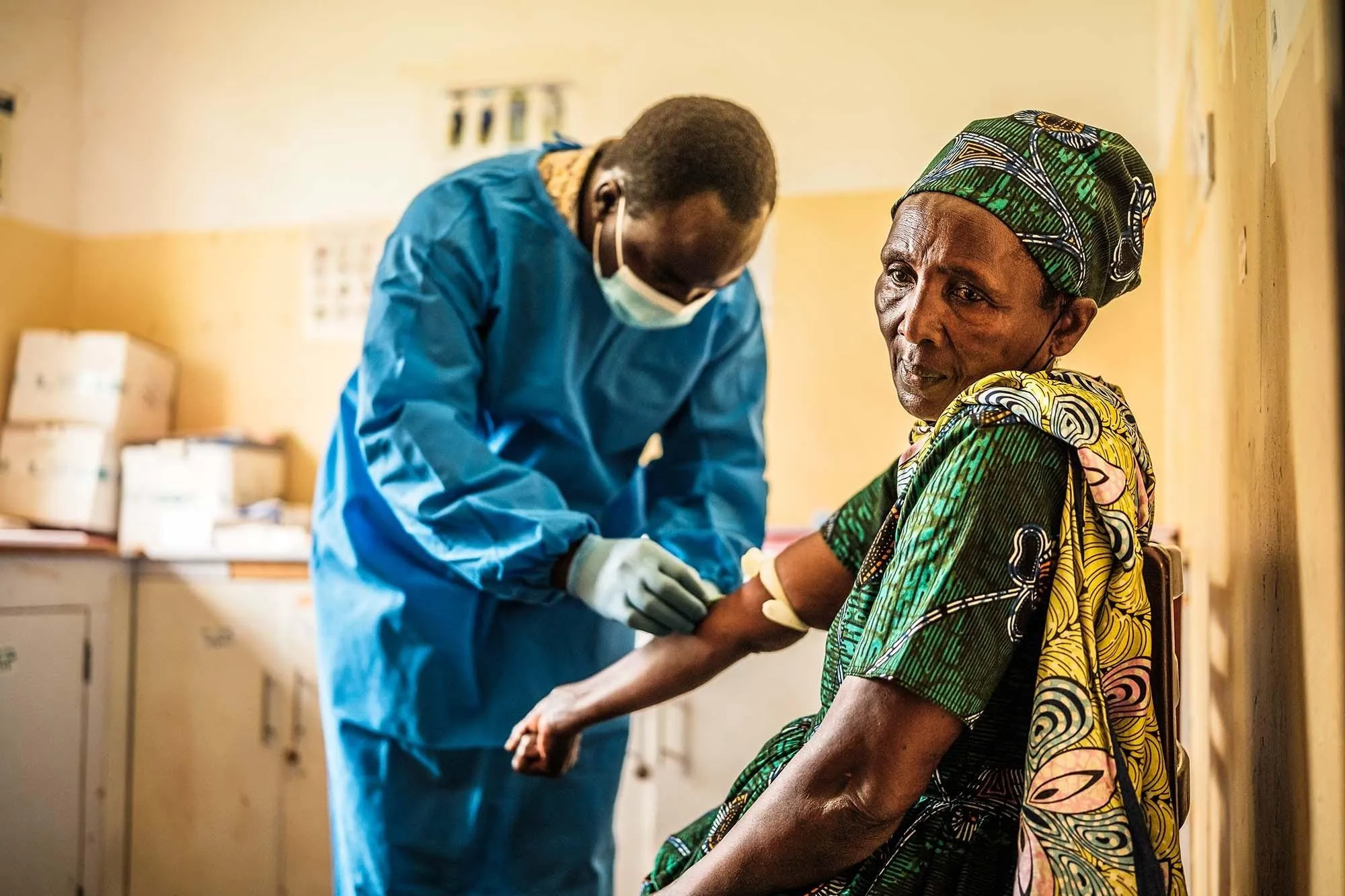
Global Health Initiatives and HIV
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) has emphasized the integral role of HIV, tuberculosis (TB), and malaria in meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These intertwined issues require a comprehensive approach, especially in light of climate change, which increasingly displaces communities and amplifies health vulnerabilities.
Strategies to Combat TB and Malaria
- Innovative Treatments: Research into new treatments for TB and malaria remains a priority.
- Funding Initiatives: The Global Fund plays a crucial role in sustaining financial support.
- Community Outreach: Engaging communities affected by these diseases fosters awareness and prevention strategies.
Addressing Climate Change in Health Policies
- Integration of Health Policies: Climate change must be considered in public health strategies.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Ongoing research is necessary to monitor the impact of climate-related health issues.
- Collaboration Across Sectors: Partnerships between health organizations and climate agencies enhance efforts.
As the UNGA leads global discussions on health, it becomes imperative to integrate innovative solutions to manage HIV, TB, and malaria while addressing the challenges brought about by climate change.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.