Impact of Amyloid-β and Tau on Cognitive Function in Alzheimer’s Disease
Thursday, 19 September 2024, 22:01
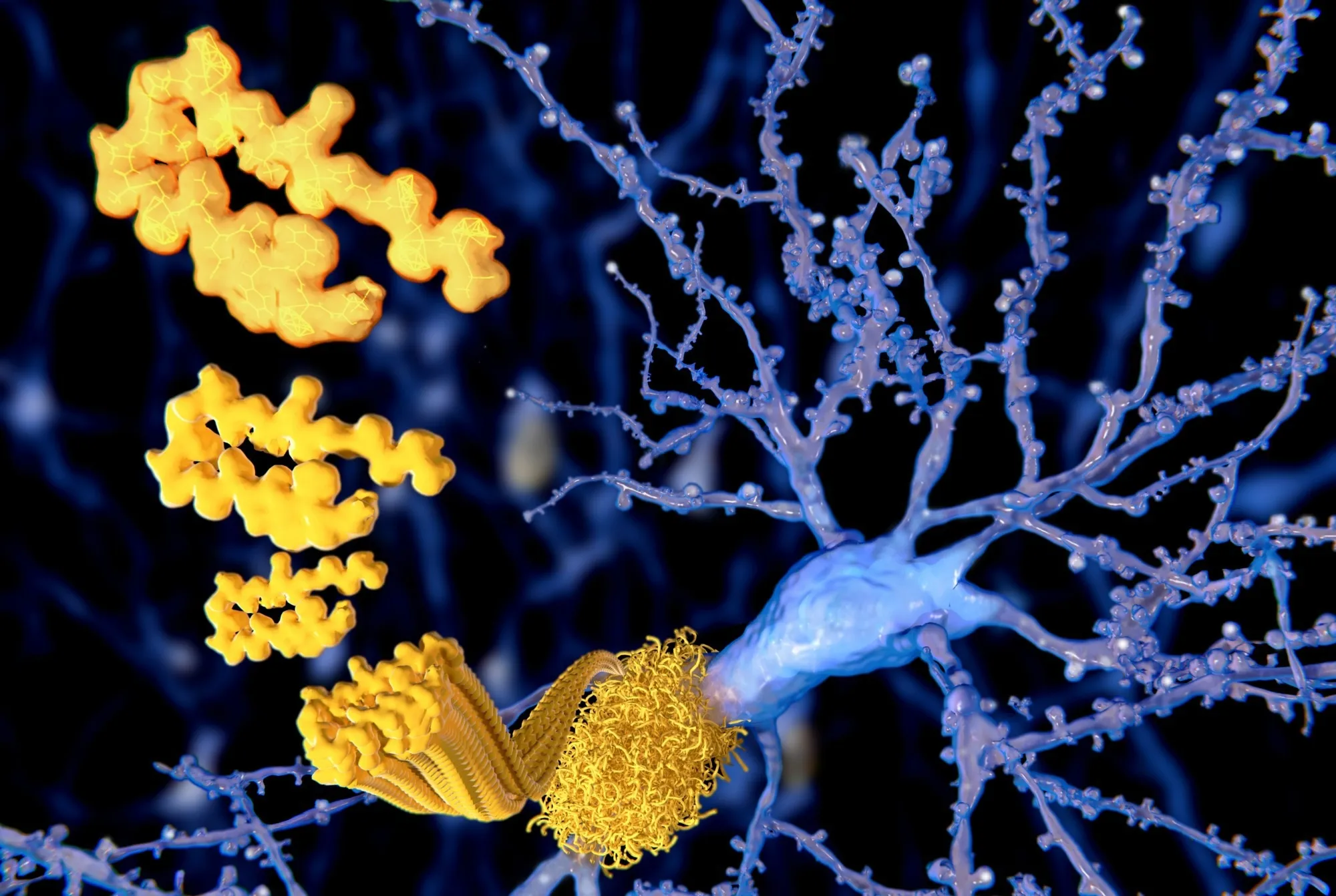
Understanding the Role of Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer's Disease
Research indicates that amyloid-β and tau significantly impact neurons in the cortex, leading to cognitive decline in older adults at risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Their interaction drives alterations in neurophysiology, contributing to dementia pathology.
Key Findings
- Amyloid-β disrupts cognitive function, leading to abnormal neuronal activity.
- Elevated levels of tau further exacerbate these changes.
- Imaging studies reveal a correlation between these pathologies and early dementia symptoms.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.