Medicine Research: High Serum Magnesium Levels Linked to Increased Mortality in Sepsis
Understanding the Impact of Magnesium Levels in Sepsis
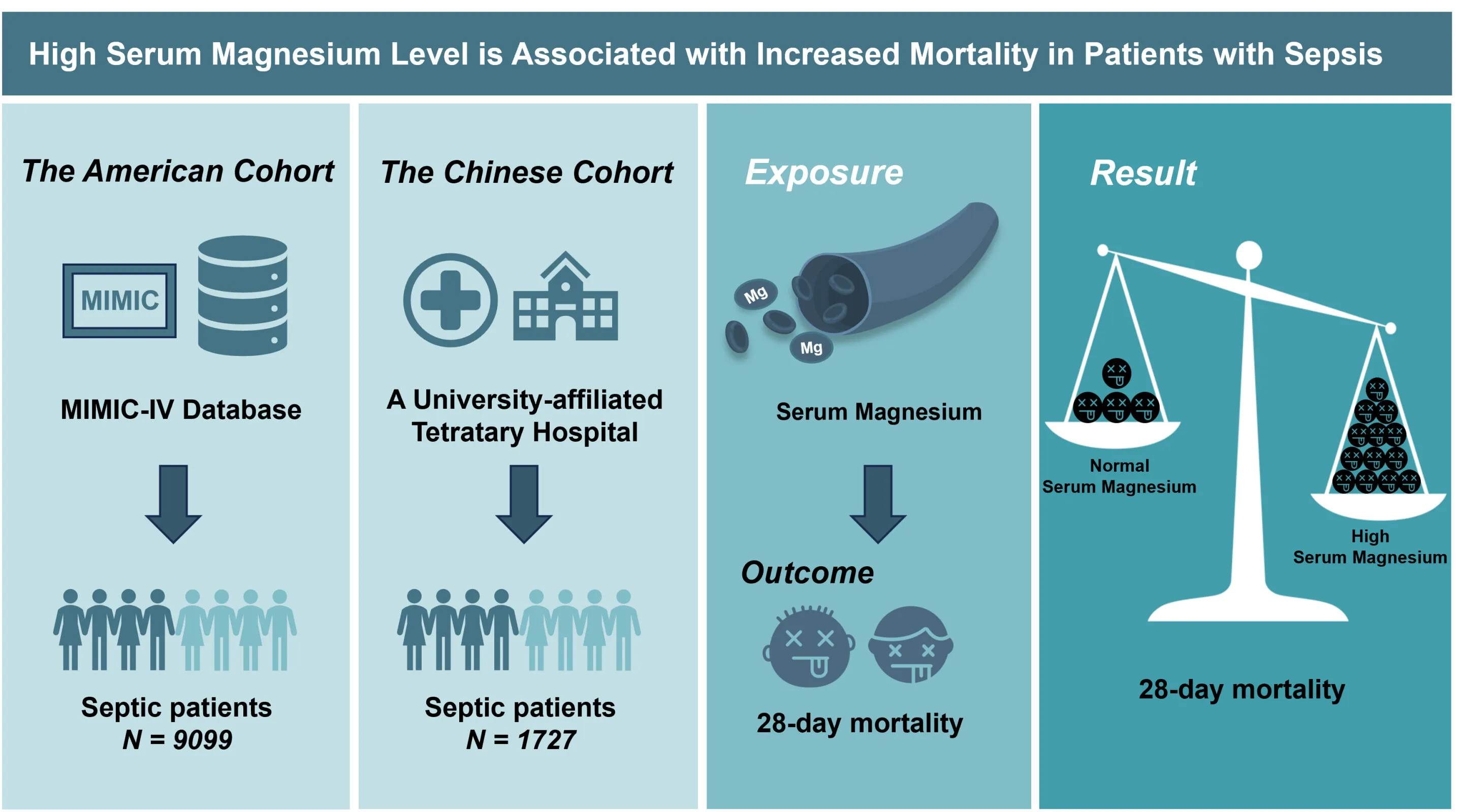
Sepsis is one of the most common life-threatening conditions in intensive care units, with approximately 48.9 million cases reported worldwide in 2017, accounting for 19.7% of total global mortality. Recent medicine research has shed light on the critical role of serum magnesium levels in septic patients.
The Link Between Magnesium Levels and Mortality
High serum magnesium levels have been associated with increased mortality in patients experiencing sepsis. This finding raises significant questions regarding the management and treatment of sepsis in healthcare settings.
Key Findings from Recent Studies
- Sepsis Prevalence: High incidence in intensive care units.
- Mortality Trends: Elevated serum magnesium correlated with worse outcomes.
- Future Research: Needed to explore potential treatment implications.
This study underscores the importance of closely monitoring serum magnesium levels in patients afflicted with sepsis and prompts further investigation into improving health outcomes.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.