Medicine Research: The Role of Parkinson's-Related Protein in Cancer and T Cell Activation
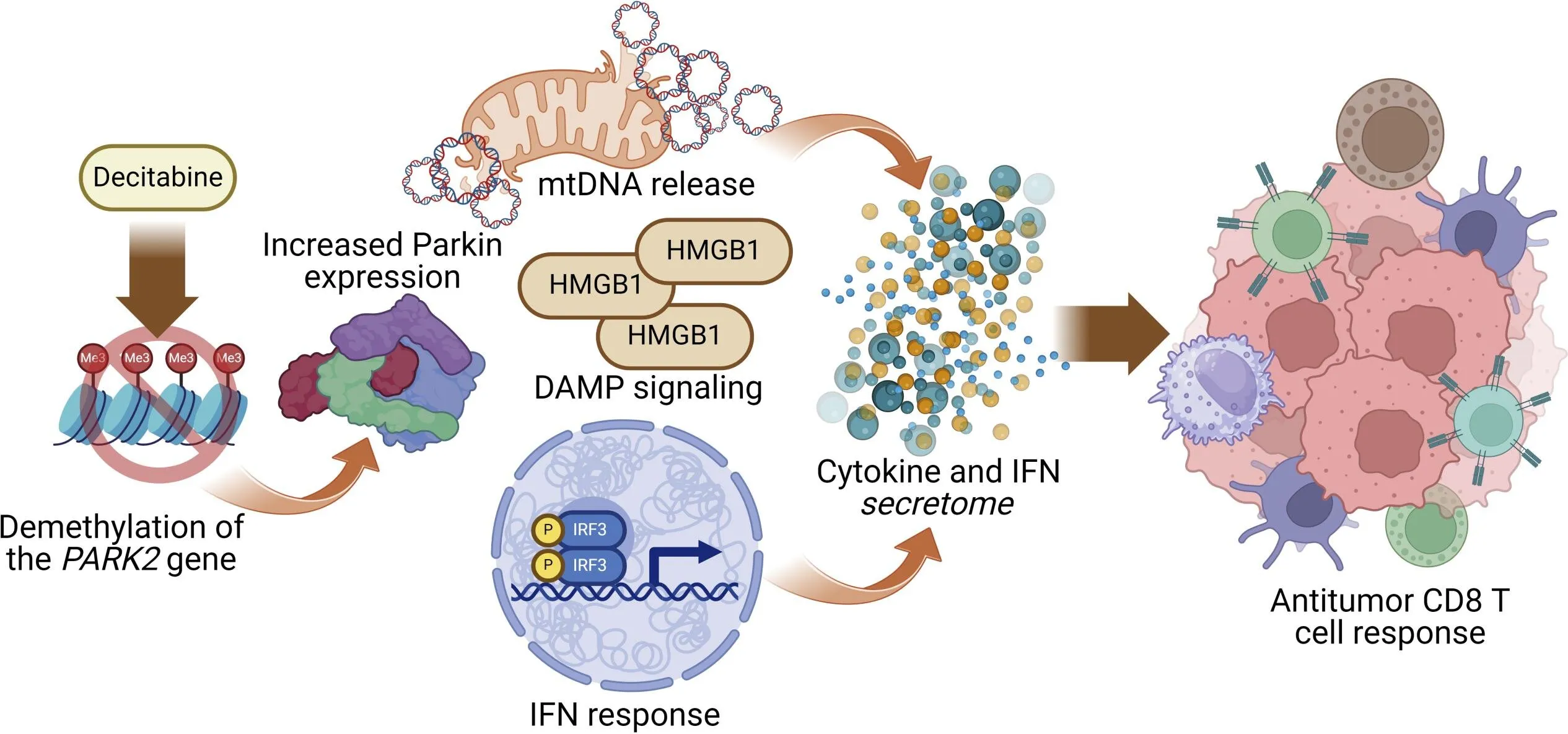
A recent study conducted by the Wistar Institute highlights critical findings in health research. Researchers have uncovered the role of Parkin, a protein associated with Parkinson's disease, in mediating the body's innate immune response to cancer. This research serves as a notable example of how medicine science can intersect with immunology and cancer biology.
The Role of Parkin in T Cell Activation
Parkin is not only involved in neurodegenerative diseases but also plays a significant role in the activation of T cells that fight tumors. The importance of understanding this multifaceted role cannot be overstated, as it opens new avenues for health science and potential therapeutic approaches.
Implications for Future Research
- Understanding immune responses in cancer
- Exploring new cancer therapies
- Investigating neuroimmune interactions
This groundbreaking research exemplifies the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration within medicine research, offering a glimpse into future health research news.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.