Health Research Insights: Brain Scans Reveal Schizophrenia Effects
Key Findings in Health Science
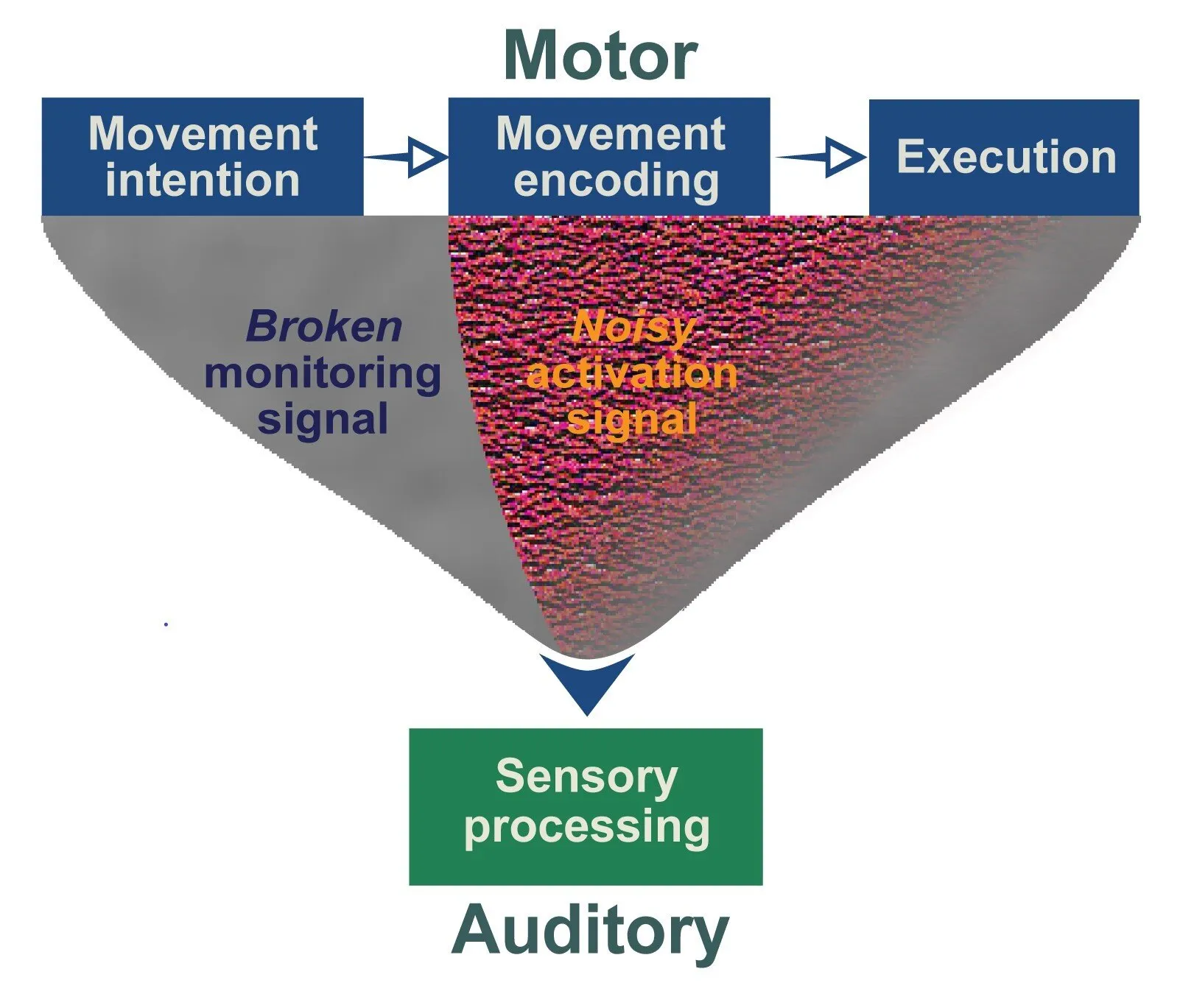
Recent medicine research highlights that auditory hallucinations among individuals with schizophrenia are attributed to abnormalities in two key processes within the brain. First, a "broken" corollary discharge fails to suppress self-generated sounds, leading to confusion in auditory perception. Second, a "noisy" efference copy amplifies external noises, making it challenging for patients to distinguish between reality and hallucinations.
Implications for Medicine Science
- Enhanced Understanding: The findings provide crucial insights into the neurobiological underpinnings of schizophrenia.
- Potential Treatments: These insights could inform future health research aimed at developing targeted therapies for managing auditory hallucinations.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.