Health Research: Reducing Sitting Time Can Prevent Back Pain
Understanding the Impact of Sitting on Back Pain
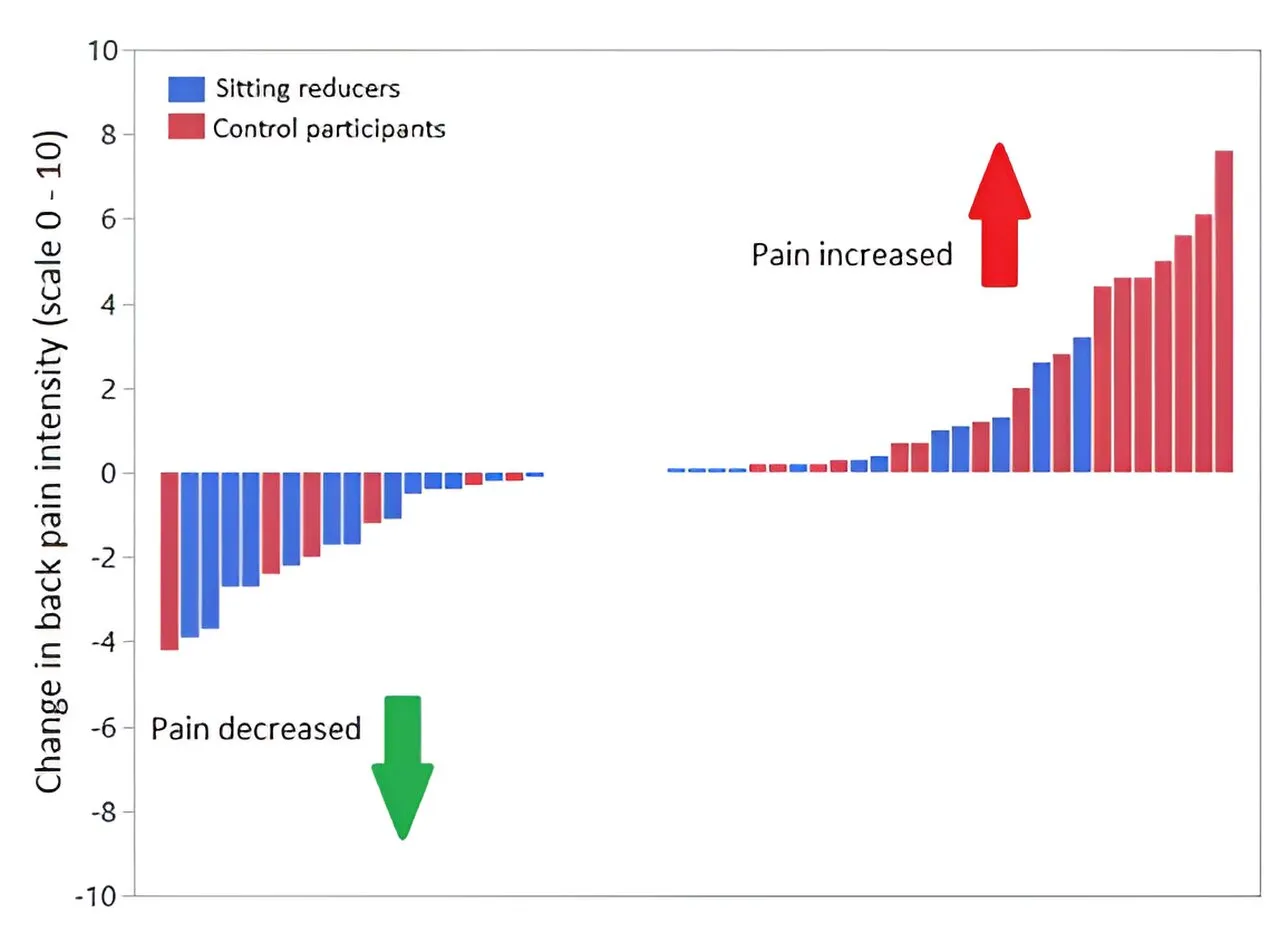
Recent health research has highlighted a strong correlation between prolonged sitting and the exacerbation of back pain. The study conducted by the University of Turku emphasizes that reducing sitting time by approximately 40 minutes each day can lead to significant improvements in spinal health over a period of six months.
Key Findings from the Study
- Daily movement is essential in combating the onset of back pain.
- Sitting for long periods increases strain on the back, leading to discomfort.
- Integrating more standing or walking breaks throughout the day can enhance overall health.
This medicine research news contributes to the growing body of evidence underscoring the significance of an active lifestyle.
Implications for Health Science
The implications of these findings are profound for health science professionals and individuals alike. Recognizing the importance of reducing sedentary behavior can promote wellness and decrease instances of chronic back conditions. This research serves as a reminder that small daily changes can lead to significant health benefits.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.