Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Impact on Cognitive Function
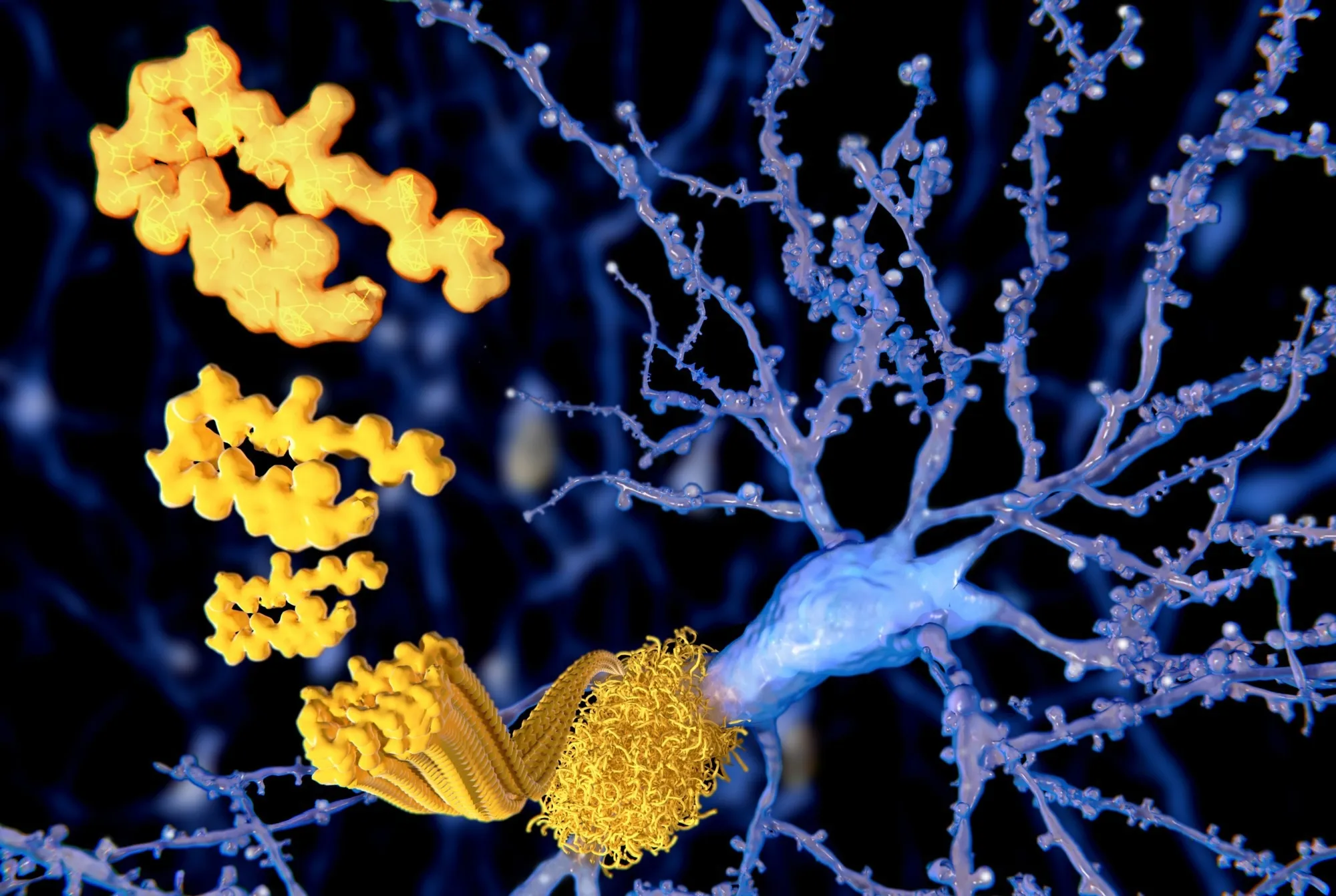
The Role of Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer's Disease
Amyloid-β and tau are two critical proteins involved in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. These proteins interact to create hyperactivity in brain neurons, leading to alterations in cognitive function.
Imaging Techniques and Neurophysiology
- Advanced imaging provides insights into the cortex's changes.
- Research shows frequency patterns of brain activity affected by amyloid-β.
- Understanding neurophysiology can aid in early detection of Alzheimer's.
Pathological Changes and Cognitive Decline
The disruption caused by amyloid-β and tau results in significant impacts on cognitive health:
- Cognitive function diminishes as dementia progresses.
- Neurotransmitter imbalances due to neuronal changes.
- Engagement in regular mental exercises may mitigate some decline.
Continued research into these interactions is essential for developing interventions aimed at preserving brain function in at-risk populations.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.