Investigating Medicine Research: How Bacterial Infections May Trigger Type 1 Diabetes
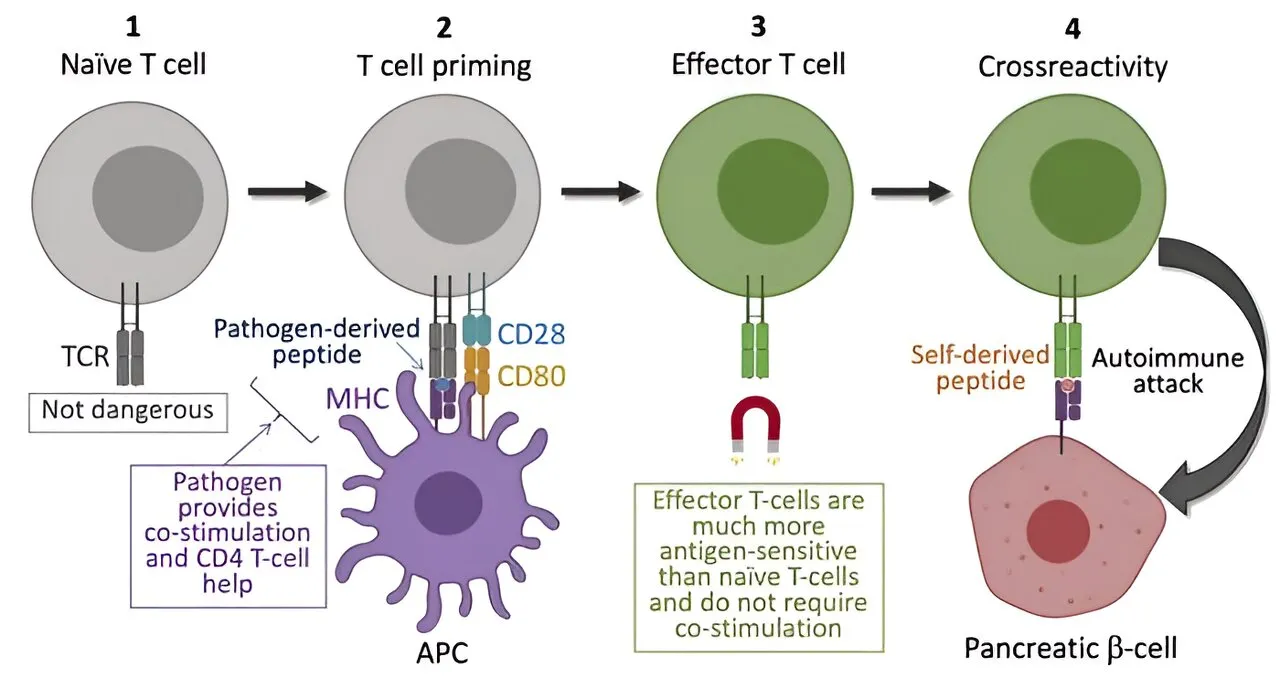
Exploring the Connection Between Bacterial Infections and Type 1 Diabetes
Recent medicine research suggests that bacterial infections could play a significant role in triggering type 1 diabetes. This groundbreaking health research news focuses on the alarming discovery that proteins derived from bacteria can activate the immune system, potentially leading to the destruction of insulin-producing cells.
The Risks of Bacterial Exposure
Healthcare scientists are increasingly aware of how bacterial exposure affects health. Keywords such as health research emphasize the necessity for ongoing studies in this domain. As investigations continue, several pivotal factors have been identified:
- The role of specific proteins derived from bacteria
- Immune response mechanisms linked to type 1 diabetes
- Potential for future prevention strategies based on new findings
Implications for Health Science
This revolutionary medicine science finding might redefine approaches to type 1 diabetes treatment and prevention. Continuous health research will be key in uncovering the broader implications and potential therapeutic interventions.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.