Public Health Strategies for RSV: Identifying Vulnerable Children
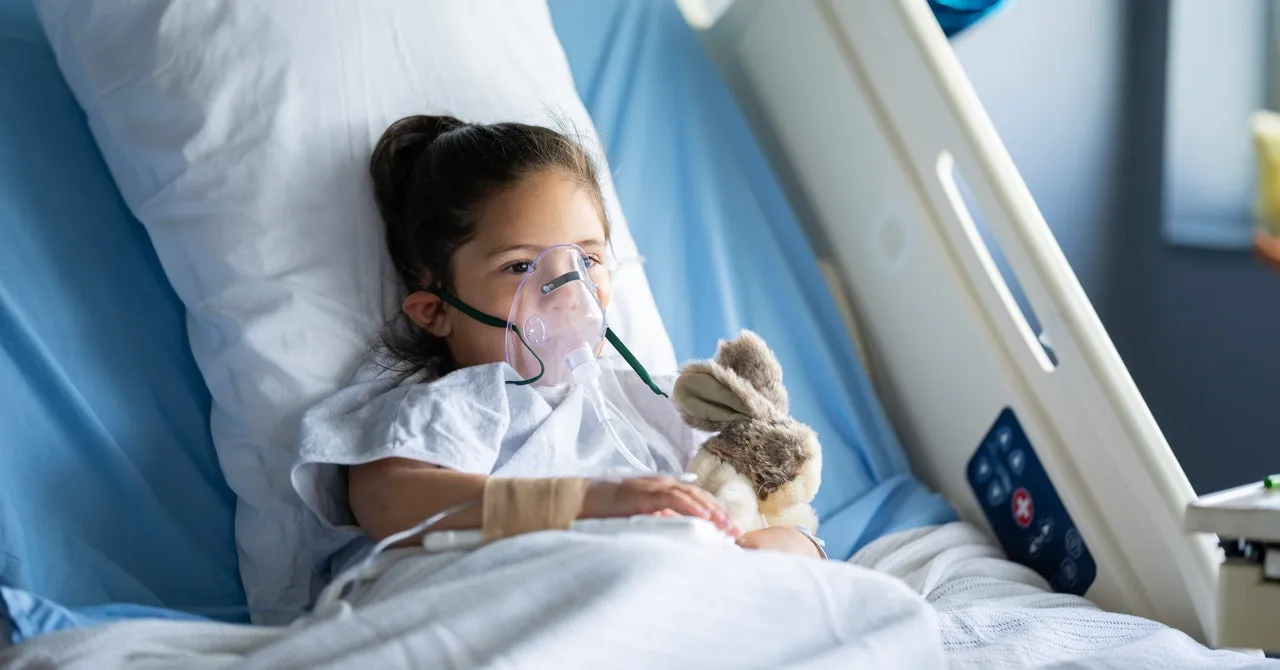
Understanding RSV and Its Impact on Children
RSV, or respiratory syncytial virus, is a common yet unpredictable disease that nearly every child will encounter by the age of two. While most children will exhibit mild symptoms, severe lung disease can develop, resulting in over 100,000 infant deaths annually worldwide. Shockingly, 80% of affected children appear healthy prior to hospitalization.
Utilizing Science and Data for Public Health
Researchers are employing machine learning algorithms and statistical models to recognize risk factors associated with RSV. For instance, a recent tool from Vanderbilt University identifies 19 specific risk factors, allowing healthcare providers to prioritize infants most vulnerable to severe RSV infections.
- Risk factors include prenatal smoking and low birth weight.
- Innovative vaccines and treatments, such as Abrysvo and Beyfortus, aim to provide protection.
- Access to RSV immunizations remains a challenge, particularly in low-income countries.
Future Directions in RSV Research
As research progresses, the development of tools to assess a child's immune response at hospital admission offers hope for more effective triaging and treatment strategies. Such advancements could alleviate anxiety for families facing RSV uncertainties.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.