Exploring Maximum Inspiratory Pressure Evaluation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
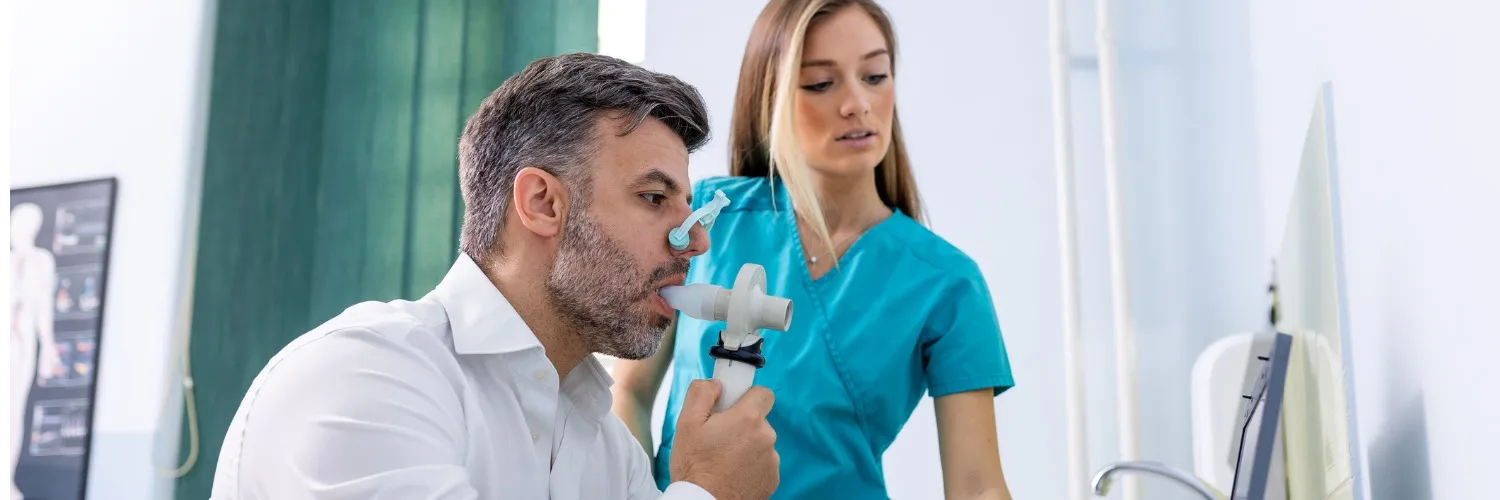
Understanding Maximum Inspiratory Pressure in COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a debilitating condition that impairs lung function and quality of life. With the need for effective assessment, the new protocol introduces an innovative approach to evaluate maximum inspiratory pressure.
Study Overview
The research conducted by Raúl Fabero-Garrido, MSc, and his team aims to explore alternatives to the traditional manovacuometer method for measuring maximum inspiratory pressure. This shift in methodology could provide more accurate and reliable assessments tailored for COPD patients.
Key Findings
- Enhanced Assessment: Utilizing a new protocol may lead to improved clinical outcomes.
- Alternative Measures: Evaluating maximum inspiratory pressure with fewer constraints.
- Future Implications: Potential changes in respiratory therapy practices for COPD.
Implications for COPD Management
This innovative approach signifies a critical advancement in how healthcare practitioners measure and understand the respiratory challenges faced by COPD patients. For those who battle this disease, advancing testing protocols may pave the way for improved treatment outcomes.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on the content of this site. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment. We source our news from reputable sources and provide links to the original articles. We do not endorse or assume responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained in external sources.
This article was prepared using information from open sources in accordance with the principles of Ethical Policy. The editorial team is not responsible for absolute accuracy, as it relies on data from the sources referenced.